|
|
|
Kinematics:
Kinematics
is the physics of motion!
Similarities
and differences between distance and displacement:
|
|
Distance |
Displacement |
|
Units: |
Meters |
Meters |
|
Quantity: |
Scalar |
Vector |
|
Representation: |
By
number and unit e.g.
5m 10km |
Represented
by a vector arrow |
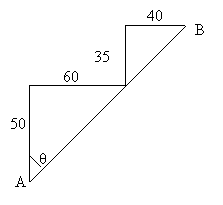
Distance = 50 + 60 + 35 + 40
= 185 m
Dispalcement = (√502+602)
+ (√352+402)
= 131. (3sf)
tan-1 100/85
= 49.6°
Vector is 131m at angle of 49.6° due north
Equations of motion for an object traveling at
constant acceleration:
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
t =
time taken
s = displacement
a = acceleration
Acceleration = Δ Velocity / Δ
Time
at = v - u
v = u + at EQUATION 1
Average velocity = distance moved / time
taken
(u + v) / 2 = s / t
therefore: s = (u + v) / 2 x t EQUATION 2
t = 2s / (u + v)
v = u + a (2s / (u + v))
v u = a (2s / (u+v))
(v-u)(v+u) = 2as
v2 u2 = 2as
v2 = u2 + 2as -
EQUATION 3
From 2)
s = (u+v) / 2
x t
but we can sub in equation 1 for the v, so we
get:
s = (u + u + at)t / 2
s = (2u + at)t / 2
s = 2ut + at2 / 2
s = ut + ½at2 EQUATION 4